A Brief Overview of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis is an autoimmune disorder and does not have any cure. It is only possible to reduce the severity of the symptoms, which offers the patient a better quality of life. Rheumatoid Arthritis primarily affects the joints. It can also affect the lungs, voice box, and eye.
Symptoms
The distinguishing feature of Rheumatoid arthritis is that it affects both hands and both legs. There is swelling, pain, redness and tenderness in the finger joints, wrist, elbow and knee. The feet, hip, neck and even the jaw can be affected. Unfortunately, the exact cause for Rheumatoid arthritis is unknown. A gene alteration is the most likely cause of this autoimmune disorder which predominantly affects women.
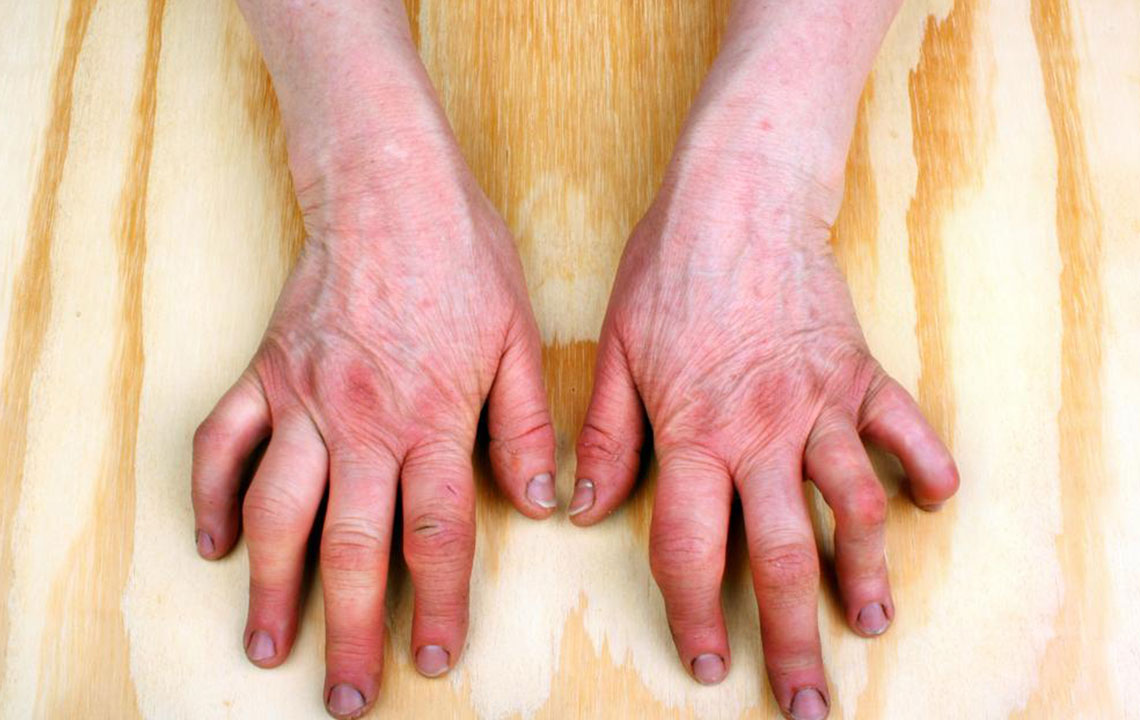
As the symptoms show up differently in each person, a combination of tests help to draw the conclusion that a person is suffering from Rheumatoid Arthritis. Most often, the evident Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis help to diagnose the condition.
There are some signs when rheumatoid arthritis affects the joints. Inflammation is accompanied by:
Stiffness
There is decreased mobility in the joints. Especially during mornings, it gets pretty difficult to use your joints. The stiffness lasts for a long time, and may last more than an hour, before you find your joints loosening up.
Redness and Warmth
The affected joints appear red and you can feel a warmth when you touch the joints.
Swelling
Swelling is a characteristic of any form of arthritis. When it comes to signs of rheumatoid arthritis, the fluid enters the joint and makes it puffy.
Pain
Pain in the joints is unavoidable. Inflammation inside the joint makes it tender and sensitive. Over a period of time, the joints experience damage and results in pain.
Rheumatoid arthritis can not only affect the joints, but the entire body as well. In such cases, the symptoms manifest as fatigue, muscle ache, sickness, diminished appetite that can lead to weight loss.
Some people get rheumatoid nodules , bumps under the skin, particularly on the elbows.
Your immune system is affected when you suffer from signs of rheumatoid arthritis. If the swelling persists for a longer duration, and you experience joint stiffness in the mornings, it can be an indicator of rheumatoid arthritis.
However, there is no single diagnostic test that can pinpoint to this condition. A combination of tests, which include blood test to check the presence of RF factor and Antinuclear antibodies, are co-inferred along with other tests and reports, to confirm the condition.
Treatment Options
Treatment includes medication, regular exercise and occupational therapy. In the case of joint damage, surgery may be needed. Early diagnosis and treatment can help in managing the condition to a large extent. In fact, in many cases, treatment has helped to slow down the progress of joint damage.
Prescription Drugs
Pain and inflammation are the most common symptoms. Non Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs ( NSAIDs) help to reduce the pain and inflammation. But, these drugs in no way halt the process of joint damage. Additional prescription drugs need to be taken to arrest further joint damage. The flipside of taking NSAID is a raise in blood pressure, stomach irritation, bleeding and ulcers.
Other category of drugs called, DMARDs, (Disease Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs) help to slow down or stop the progress of the disease. If inflammation persists, other types of DMARDs are prescribed. Usage of DMARDs brings down the symptoms significantly, but its usage is linked to infection and a host of other side effects.
If NSAIDs and DMARDs fail to ease the symptoms and signs of rheumatoid arthritis, biologics are prescribed. Biologics are genetically engineered proteins, which block specific parts of the immune system that cause the inflammation and helps to slow or stop rheumatoid arthritis. On the negative side, they raise the risk of infection, as the biologics suppress the immune system.
Steroids are used when there is a flare. Steroids should be taken when symptoms and signs of rheumatoid arthritis are severe, as they can help to significantly reduce the pain and inflammation.
Physical and Occupational Therapy
In addition to medication, physical therapy reduces joint stiffness and improves mobility. Both physical and occupational therapy are necessary adjuncts to rheumatoid arthritis treatment plan. An exercise plan charted by physical therapists can guide you to moving the joints. You can also apply hot and cold compress to ease the pain. Occupational therapists can guide you in handling your daily tasks with ease.
Cognitive therapy also helps in pain management. Since pain is an inherent part of rheumatoid arthritis, this therapy lays emphasis on your emotional and psychological well being.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a debilitating condition indeed, but with timely diagnosis and treatment, it is possible to reduce the severity of the symptoms.

